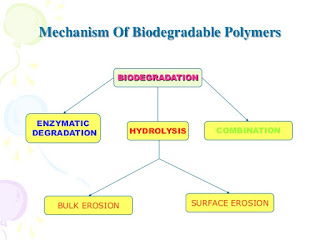
ICH GUIDELINE FOR STABILITY TESTING

· Describes regarding sampling times, storage conditions& specific test parameters for each dosage form. · The FDA & The expert working group of the ICH of technical requirements for the registration of pharmaceuticals for human use have published guidelines for conducting the actual studies. · ICH guideline as follow, o Quality Guidelines “Q” (chemical and pharmaceutical QA) o Safety Guidelines “S” (in vitro and in vivo pre-clinical studies) § covering Carcinogenicity Testing, Genotoxicity Testing, § Toxicokinetics and Pharmacokinetics ….. etc. o Efficacy Guidelines “E” (clinical studies in human subject) § Covering clinical safety, Dose Response Studies, Good § Clinical Practices, Clinical evaluation …. etc. o Multidiscipl...