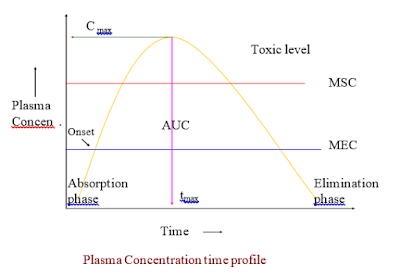
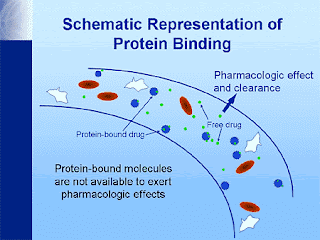
VOLUME OF DISTRIBUTION

The volume of distribution (VD) , also known as apparent volume of distribution, is used to quantify the distribution of a medication between plasma and the rest of the body after oral or parenteral dosing. It is defined as the volume in which the amount of drug would need to be uniformly distributed to produce the observed blood concentration. Volume of distribution may be increased by renal failure (due to fluid retention) and liver failure (due to altered body fluid and plasma protein binding). Conversely it may be decreased in dehydration. EQUATION: The volume of distribution is given by the following equation: Therefore the dose required to give a certain plasma concentration can be determined if the VD for that drug is known. The VD is not a physiologic value; it is more a reflection of how a drug will distribute throughout the body depending on several physicochemical properties, e.g. solubility, charge, size, etc. ...