Biodegradable Polymer: Introduction
Definition: A polymer
that are degradable in-vivo, either by enzymatically or
non-enzymatically, to produce biocompatible or nontoxic by-products.
Biodegradation: A natural process by which organic
chemicals are converted to simpler compound through elemental cycles such as
the carbon, nitrogen and Sulphur cycles.
- Microorganism plays a central role in the biodegradation process.
- Bio degradation occur in two steps:
- 1st step From Fragmentation of the polymer into lower molecules:
- By abiotic reaction i.e. oxidation, photo degradation, hydrolysis.
- By biotic reaction i.e. degradation by microorganism.
- 2nd step: Bio Assimilation of the polymer fragments
- Biodegradability of the polymer depends on
- Its origin & chemical structure & also environmental condition
- Biodegradable polymers are capable of being cleaved into biocompatible by-product through chemical or enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis
- Advantages of Biodegradable polymer:
- Provide constant controlled rate for long time
- Metabolized by-product is non-toxic and easily remove by body extraction
- Dose dumping not exhibit
- No surgical removal of implanted device
- It can be used for targeted drug delivery
- Disadvantages of Biodegradable polymer:
- Burst effect at initial dose
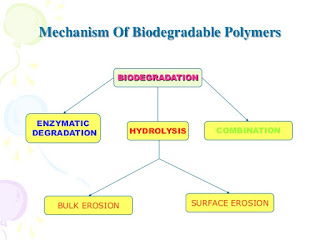
- Mechanism of drug release from Biodegradable polymer:
- This polymer degrades within body as a result of natural biological process.
- Most biodegradable polymer degrades through hydrolysis process.
- Biodegradable polymer undergo degradation in four steps
- Hydration
- Strength loss
- Loss of mass Integrity
- Mass loss
- Hydration:
- It is variable in rate, degree and is dependent upon the nature of polymer.
- In this step, disruption of Vander Waal’s bond or hydrogen bond is broken.
- Strength loss
- In this step, the covalent bond is broken.
- The strength loss rate is dependent upon the temperature, pH and degree of crystallinity.
- More crystalline species may be expected to maintain their strength for longer period of time compare to those of amorphous.
- Loss of mass Integrity
- In this step more and more covalent bond is broken and polymer is degraded to a molecular weight level.
- This step is more important in degradation.
- Mass loss:
- This step involves the complete removal of Polymer from the tissue.
- It occurs either by solubilization of small units or by phagocytes
- Sometime the polymer mass may be removed from site, without actual reduction in their length, thought solubilization that involve side chain modification
- Factors affecting Biodegradation of polymer:
- Chemical structure
- Chemical decomposition
- Present of ionic groups
- Molecular weight
- Morphology
- Site of implantation
- Mechanism of hydrolysis
- Hydrophilicity
- Classification of biodegradable polymers:
- Natural polymer:
- Guar gum, Acacia, Karaya, Tragacanth, Xanthan, Albumin, pectin, starch, gellen etc.
- Prime advantage include biodegradation in natural products, easy availability, absense of toxicity and antigenicity
- Albumin micro spheres have been employed to deliver many drugs like hematoprophyrin, sulphadiazine, and prednisolone, 5-flurouracil
- Semisynthetic polymer:
- Cellulose derivatives:
- Cellulose is insoluble in water and most commom solvents
- Have poor solubility
- Chemically modified cellulose have a good properties,
- It include; CMC, MC, HEC, HPMC etc
- Collagen:
- Have good biocompatibility, low toxicity, degradation on implantation and gelling ability
- Gelatin:
- It has been employed as matrix and coating material.
- It offers advantage like low antigen profile ,poor binding to drug, low temp
- So reduce to chances of drug degradation
- Chitin and chitosan:
- Chitosan has been administered as excipients for oral drug formulations.
- It is used as direct tableting agent, mask bitter taste, disinyegrant & for coating.
- Have good mucoadhesive, antimicrobial and controlled release properties
- Dextran:
- Synthesized from sucrose by certain lactic acid bacteria.
- Alginate:
- Alginate micro spheres have been used for oral delivery of vaccines.
- They protect antigen/vaccine against degradation in G.I.T.
- Have good gelling ability
- Fibrinogen, Hyaluronic acid, Cyclodextrin




Comments
Post a Comment