Nano-Technology: An Overview
HISTORY
|
- Prof. Paul Ehrlich gave the
concept of “magic bullet” for drug targeting.
- Prof. Peter Paul Speiser and his co-workers developed first nanoparticles for drug delivery purpose and for vaccines in the late 1960s.
|
NANOTECHNOLOGY
|
- Nanotechnology is the design, characterization, production and application of structures, devices and systems by controlling shape and size at nanometer scale.(The Royal Society Report, July 2004)
- It is a multi-disciplinary subject involving the use of physics, chemistry, biology and engineering.
- There are two fundamentally different approaches to nanotechnology:
- “Top-down” is the production of nanoscale structures by taking a bulk material and forming it into a desired structure.
- “Bottom-up” refers to building organic and inorganic structures atom by atom or molecule by molecule.
|
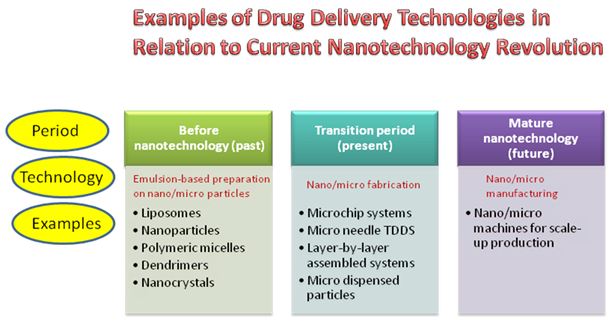
NANOPARTICLES
|
- Nanoparticles are solid colloidal particles consisting of macromolecular substances that vary in size from 10nm to 1,000nm.
- The drug of interest is dissolved, entrapped, adsorbed attached or encapsulated into the nanoparticle matrix.
- Depending upon the method of preparation, nanoparticles, nanospheres or nanocapsules can be obtained with different properties and release characteristics for the encapsulated therapeutic agent.
|
TYPES OF NANOPARTICULATE SYSTEMS
|
|
Sr. No.
|
Types of Nanoparticles
|
Material Used
|
Applications
|
|
1.
|
Polymeric
nanoparticles
|
Biodegradable
polymers
|
Controlled
and targeted drug delivery
|
|
2.
|
Solid lipid
nanoparticles
|
Melted lipid
dispersed in an aqueous surfactant
|
Least toxic
and more stable colloidal carrier systems as alternative to polymers
|
|
3.
|
Nanocrystals
& nanosuspensions
|
Drug powder
is dispersed in a surfactant solution
|
Stable
systems for controlled delivery of poorly water soluble drugs
|
|
4.
|
Polymeric
micelles
|
Amphiphilic
block copolymers
|
Systemic and
controlled delivery of water insoluble drugs
|
|
5.
|
Liposomes
|
Phospholipid
vesicles
|
Controlled
and targeted drug delivery
|
|
6.
|
Dendrimers
|
Tree like
molecules with defined cavities
|
Drug
targeting
|
|
7.
|
Magnetic NPs
|
An inorganic
core of iron oxide (magnetite) coated with polymer such as dextran
|
Drug
targeting, Diagnostic tool in biology and medicine
|
|
8.
|
Gold
nanoshells
|
Dielectric
(typically gold sulfide or silica) core and a metal (gold) shell
|
Tumor
targeting
|
|
9.
|
Nanowires or
Carbon nanotubes
|
Metals,
semiconductors or carbon
|
Gene and DNA
delivery
|
|
10.
|
Ferrofluids
|
Iron oxide
magnetic NPs surrounded by a polymeric layer
|
For
capturing cells and other biological targets from blood or other fluids and
tissue samples
|





Comments
Post a Comment