Pharmacokinetics: Physiological Model
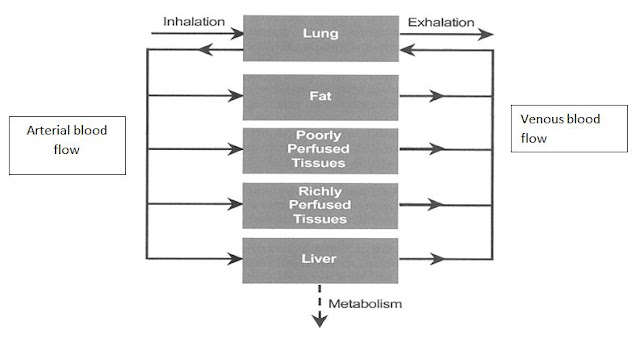
PHYSIOLOGIC MODEL
o
Also called as Blood flow rate –limited
models and perfusion rate limited models.
o
Physiological
models describe the drug disposition in terms of realistic physiological
parameters such as blood flow and tissue partition co-efficient.
o
The
number of compartments to be included in the model depends upon the disposition
characteristics of drug.
o
Organs
such as bone that have no drug penetration are excluded.
o
Most
physiologic models are based on the assumption that the drug movement within a
body region is much more rapid than its rate of delivery to that region by the
perfusion blood and, therefore the model is said to be perfusion rate limited.
The assumption is however applicable to the highly membrane permeable drugs
i.e. low molecular weight, poorly ionized and highly lipophilic drugs.
o
For,
highly polar, ionized and charged drugs, the model is referred to as membrane
permeation rate limited.
ADVANTAGES
OF PHYSIOLOGIC MODELING:
·
Mathematical
treatment is straightforward.
·
Data
fitting is not required; drug concentration in various body regions can be
depicted on the basis of organ or tissue volume, perfusion rate and
experimentally determined tissue to plasma partition coefficient.
·
The
influence of altered physiology or pathology on drug disposition can be easily
predicted from changes in various pharmacokinetic parameters since the
parameters correspond to actual physiologic and anatomic measures.
·
Correlation
of data in several animal species is possible and with some drugs, can be
extrapolated to humans.
The only disadvantage
of these comprehensive models is obtaining experimental data, which is very
exhaustive



Comments
Post a Comment